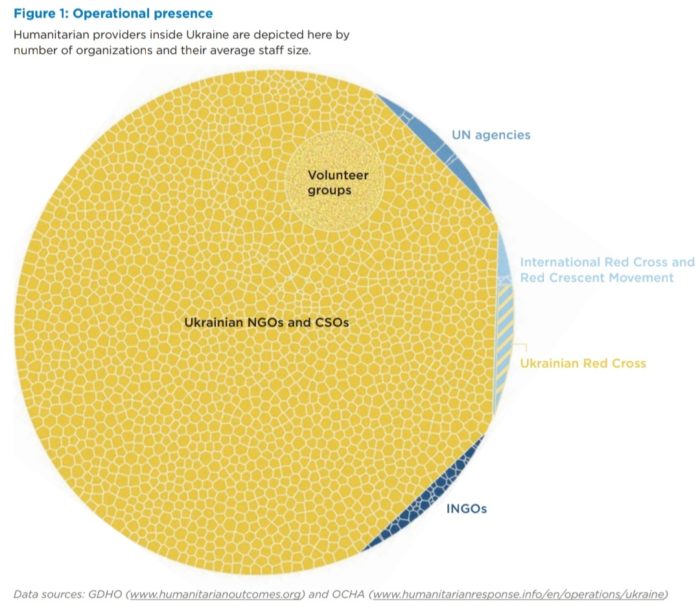
Since the beginning of the Russian invasion, virtually all humanitarian aid inside Ukraine has been implemented by local actors, not international organizations, according to the review conducted by Humanitarian Outcomes in May 2022. These included around 150 pre-existing national NGOs, church groups, and around 1,700 newly formed local aid groups.
Though UN humanitarian agencies
and international NGOs received 87% of humanitarian aid funding for Ukraine, they did not manage to effectively use these resources to support humanitarian initiatives in Ukraine.
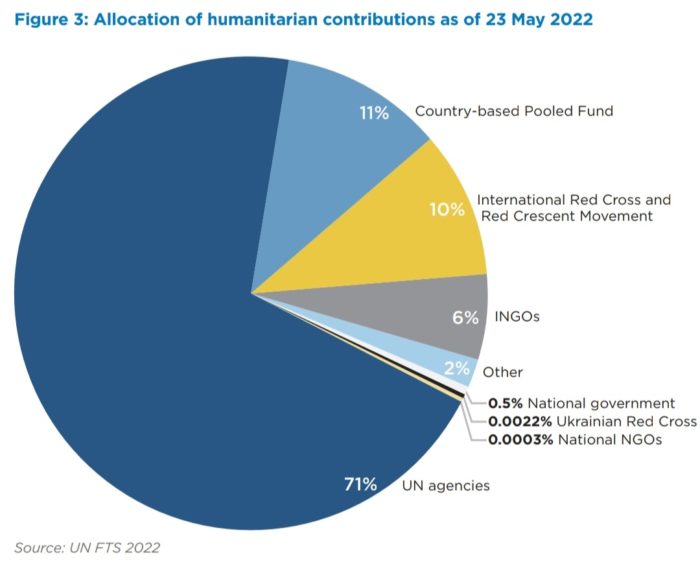
Meanwhile, Ukrainian NGOs received only 0,0003%, or $4,4 mln, of direct humanitarian aid funding
. The brief by Humanitarian Outcomes analyzes the causes of poor humanitarian response of international organizations and proposes several solutions.
Humanitarian Outcomes has conducted interviews with 60 informants from national and international humanitarian aid groups as well as donor governments and analyzed data on aid operations and funding. It concluded that UN humanitarian agencies and international NGOs faced several challenges:
- International organizations lacked preparedness and contingency planning. Though UN agencies and international NGOs had programs and staff in Ukraine, they lost much time in re-entry and scale-up, since they did not have any plan for a full-scale Russian invasion. For the first 6 weeks of the invasion, virtually all humanitarian aid inside Ukraine has been implemented by local actors – national NGOs, informal volunteer groups, and the Ukrainian government.
- International organizations did not manage to use their resources to support humanitarian initiatives in Ukraine due to financial bottlenecks. Despite raising significant sums of money by international organizations, most of the money is still unused. Small volunteer groups did not apply for funding, since compliance requirements of international organizations are too heavy and time-consuming for them.
- International organizations faced issues with the recruitment of staff due to Ukraine’s martial law, widespread mobilization, and mass emigration.
- International organizations did not manage to harmonize their cash programs with the government's pre-existing social protection mechanism, which caused the establishment of multiple distribution platforms and unhelpful competition among agencies’ separate cash programs.
- International organizations failed to provide rapid response to humanitarian needs because fiscal compliance standards are inappropriately high. Inflexible compliance regimes that are counter-productive to rapid response.
"The Ukrainian government and civil society have taken the lead and will continue to lead in the humanitarian response. The challenge for the international humanitarian system is finding how best to complement, support, and add value to national and local efforts," the report concludes.
Detailed analysis and suggested solutions are available in the review.

