Russia has found a way to neutralize NATO's most advanced weapons in Ukraine, with precision-guided munitions seeing their effectiveness plummet from 95% to just 6%, according to a senior European military expert. This breakthrough in electronic warfare is just one sign of Moscow's broader military transformation.
Colonel Dr. Markus Reisner, an Austrian General Staff officer with extensive Special Operations experience, revealed how Russia has expanded its forces to 640,000 troops while systematically dismantling Western technological advantages. With North Korea supplying 3 million artillery shells and Russian forces firing 90,000 rounds daily compared to Ukraine's 20,000, a stark resource disparity is emerging.
Speaking at Germany's Center for Military History and Social Sciences, Reisner argued the war is entering its most critical phase as five key factors loom over 2025: Western political unity after US elections, Russian domestic stability, emerging military technologies, force sustainability, and global economic conditions.

Colonel Dr. Markus Reisner of the Austrian Armed Forces. Photo via ZMSBw/YouTube.
Key points:
- Russia has shown significant adaptation capabilities, expanding its forces to 640,000 troops and effectively countering Western technology, particularly in electronic warfare - leading to severely reduced effectiveness of Western precision weapons.
- A stark resource disparity is emerging: Russia's artillery and international support contrasts with limited Western support to Ukraine.
- The war has evolved into a multi-domain conflict, featuring battlegrounds in maritime, space, and electromagnetic spheres, with commercial actors playing unprecedented roles.
- Western support follows a pattern of "helping Ukraine fight but not win," with political considerations and resource constraints limiting the delivery of decisive military capabilities.
- Looking ahead to 2025, the war’s outcome depends on five key factors: Western political unity post-US elections, Russian domestic stability, emerging military technologies, force sustainability and global economic conditions.
Evolution of Russian tactics
The Austrian military expert notes that Russia has dramatically increased its force presence from the initial 190,000 troops to approximately 640,000 personnel on the ground. He argues that this massive force expansion demonstrates Russia's commitment to a long-term campaign.
In addition, while Russia’s army has considerable issues and problems, the expert notes that it should not be underestimated, as it has shown a capacity to adapt to changing battlefield conditions and dynamics.
"The Russians have shown remarkable ability to adapt their tactics and equipment," notes Reisner. "They've modified their vehicles with additional protection against drones, saturated the electromagnetic spectrum to counter Ukrainian systems, and effectively deployed new capabilities like glide bombs."
According to Reisner, one example is the Russian ground forces' tactical approach to battlefield reconnaissance. They've implemented the use of motorcycle reconnaissance units to probe Ukrainian defenses, a technique that might seem primitive at first glance but has proven effective.
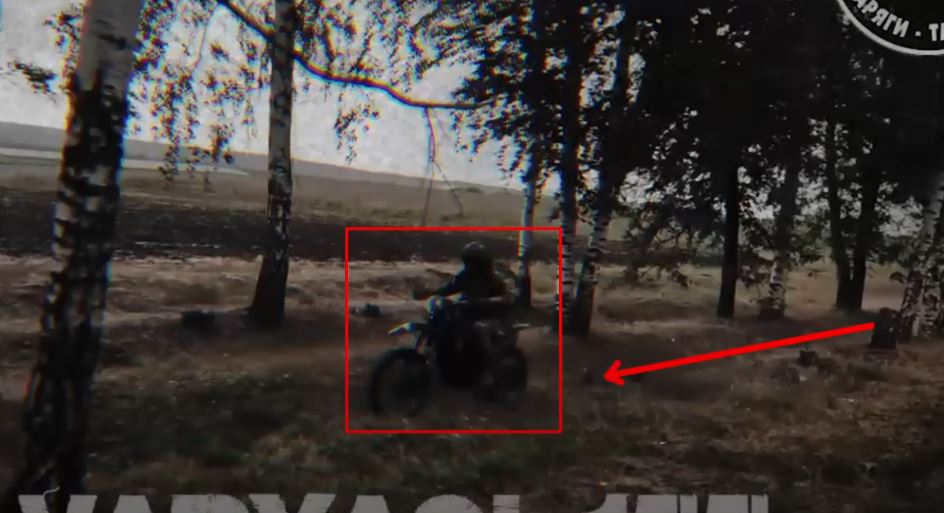

These units create a screening effect across several kilometers of the front line, allowing Russian forces to identify weaknesses in Ukrainian positions.
Although the tactic can be costly (as attested by the multitude of clips showcasing killed Russian soldiers on social media), when combined with drone surveillance, this tactic enables Russian commanders to locate vulnerable points before committing their mechanized units to the attack.
The Russian military has also demonstrated evolution in its electronic warfare capabilities. This advancement has had a drastic effect on Western-supplied precision weapons, with some systems seeing their effectiveness reduced to a fraction of their expected performance.
Multi-domain nature of war
As Reisner notes, the war has evolved to encompass multiple domains that reflect the complexity of modern warfare. This provides clues as to what to expect from warfare in the next few decades.
In the sea, Ukraine has achieved remarkable success despite lacking a conventional navy. Through innovative use of drone boats, anti-ship missiles, and special forces, Ukrainian forces have effectively contested the Black Sea, forcing the Russian Black Sea Fleet to operate at a greater distance from the Ukrainian coast.
The electromagnetic spectrum has also become a crucial battleground, with Russian forces achieving significant advantages through sophisticated jamming and countermeasures. This has not only affected tactical communications but has also degraded the effectiveness of precision-guided munitions and drone operations.
Furthermore, the space domain has also emerged as a critical factor, particularly through the role of commercial space assets. Elon Musk's Starlink system has become a vital communication backbone for Ukrainian forces, demonstrating how commercial space technology can fundamentally influence modern warfare.
However, this reliance on commercial systems also introduces new vulnerabilities, as private sector decisions can have strategic military implications (in other words, businesspeople are able to influence battlefield dynamics, based on their own political preference as to which outcome would be best in their opinion).
Drone warfare has also seen many new developments on both sides of the frontline. Wire-guided drones have been developed to avoid electronic countermeasures, for example. This relatively new technology opens up new avenues for the tactical use of weapons, with both sides experimenting with so-called "drone swarm tactics" to overwhelm the opponent's defense.
Lastly, artificial intelligence is permeating warfare just like civilian life. Recent reports note that both Russia and Ukraine are using AI for target identification.
Critical infrastructure under systemic attack
Russia's strategy of targeting Ukraine's critical infrastructure has proven quite effective and demonstrates a clear understanding of modern warfare's systemic nature. Destroying or damaging key infrastructure ensures that Ukraine faces challenges in maintaining basic services and military production capabilities.
The implications of this strategy extend far beyond immediate military considerations. Civilian populations face a lot of hours of power outages daily, creating strains on both government resources and public morale. The targeting of power generation and distribution systems has been particularly effective, with Russian forces using a combination of cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, and Iranian-supplied drones to overwhelm Ukrainian air defenses.
A war of resources, with growing disparity
The disparity in military resources has become increasingly apparent and may ultimately prove decisive in the conflict's outcome. Artillery ammunition has become a critical factor, with Western promises of support falling short of requirements.
In contrast, North Korea has agreed to supply Russia with up to 3 million artillery shells, highlighting the effectiveness of Russia's international partnerships with authoritarian regimes. Russian production of cruise missiles has reached 100-150 per month, enabling sustained pressure on Ukrainian infrastructure.
This production rate, combined with stockpiles of existing weapons and international support, allows Russia to maintain a high tempo of operations that increasingly strains Ukrainian air defenses.
Due to Russian countermeasures, the effectiveness of Western precision munitions has dramatically decreased. Excalibur-guided artillery shells, once boasting a 95-98% success rate, now achieve only 6% effectiveness.
This degradation of precision weapons' capabilities has forced Ukrainian forces to rely more heavily on conventional artillery, exacerbating their ammunition shortage. In general, Reisner sums up that the resource disparity extends to several critical areas, and can be summarized as follows:
Artillery systems:
Trending Now
- Russian forces firing 90,000 rounds per day vs. Ukrainian 20,000
- North Korean supply of 3 million artillery shells to Russia compared to insufficient Western deliveries to Ukraine
- Iranian provision of drone technology and components to Russia
- Chinese supply of electronic components and raw materials to Russia
- Russian domestic production increases in key ammunition types
Precision-guided munitions:
- HIMARS effectiveness was reduced by 60% due to Russian countermeasures
- Storm Shadow/SCALP cruise missiles are limited by availability or held back for fear of escalation
- Excalibur-guided artillery shells show only 6% effectiveness
- Reduced effectiveness of Western anti-tank guided missiles
- Limited availability of Western air defense missiles Western support leaves Ukraine short of what it needs
Western military support has followed a careful calibration that reveals broader strategic considerations.
This has resulted in a measured approach to weapons deliveries that often leaves Ukraine short of the capabilities needed for decisive offensive operations. The delivery of advanced systems frequently comes with significant delays and limitations. Training requirements for Western equipment create additional timeline challenges, while restrictions on certain weapons systems and capabilities reflect concerns about escalation.
As Reisner notes, "Ukraine receives what it needs to fight, but not what it needs to win," highlighting the complex political calculations behind Western support decisions.
As Reisner argues, the limitations of Western support are evident in several areas:
Equipment constraints:
- Limited availability of spare parts
- Challenges in the maintenance of Western systems
- Incompatibility between different NATO systems Limited ammunition supplies for Western weapons
- Training requirements delaying deployment
Political considerations:
- Concerns about escalation with Russia in the US and Europe Impact of domestic political cycles (short-term goals)
- Economic constraints on support levels
- Competition with other global commitments
- Shifting public opinion in supporting countries
Looking ahead: 2025 and beyond
The strategic outlook for 2025 presents several critical challenges for both sides.
Reisner says that Ukraine seems to be shifting towards defensive operations, reflecting the reality of resource constraints and the need to rebuild combat power for any possible counter-operations next year. This defensive posture will test Ukraine's ability to maintain territorial control while preserving forces for future operations.
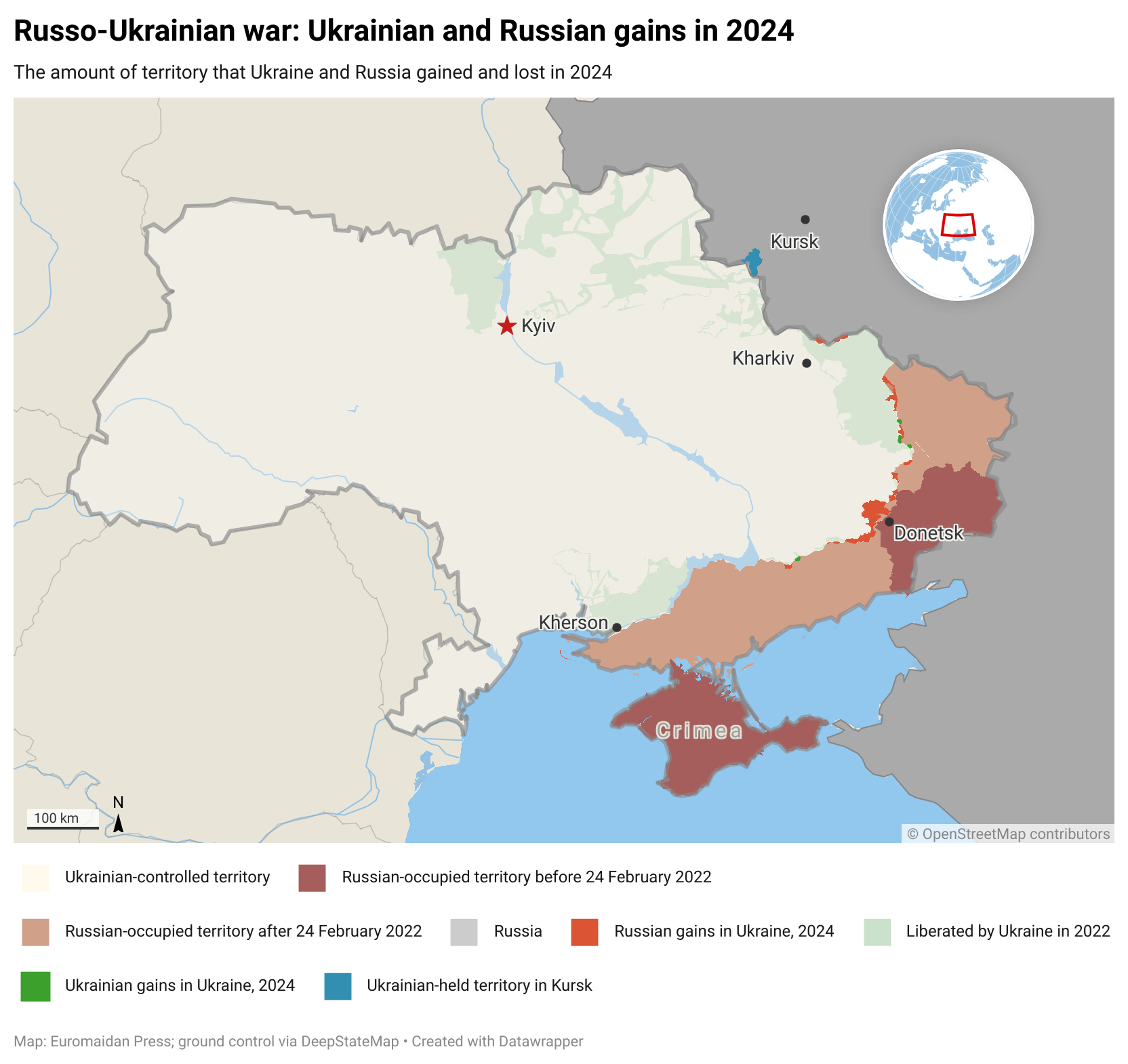
Russia, meanwhile, shows growing confidence in its attrition strategy. Its strengthening international partnerships, particularly with China, Iran, and North Korea, provide access to resources and technology that help circumvent Western sanctions. The Russian military industry has adapted to wartime requirements, increasing production of key weapons systems and developing new capabilities based on battlefield experience.
Furthermore, there are increasing signs that even Russia, with its traditional advantage in manpower, is starting to implement desperate measures as the war proves to be very deadly in nature. In addition, one of the reasons North Korean soldiers are currently fighting against Ukraine is because Russia fears the consequences of further mobilization of Russian society for the war.
In short, questions arise as to how long Russia will be able to keep up its combat operations before it starts to break down under the weight of the increasing demands of war.
In general, the military expert argues that military considerations, as well as larger strategic ones, should be taken into account. These issues act like force multipliers for the war as a whole and can move the outcome in a particular direction.
With regard to military considerations, Reisner sums up that attention should be paid to the following areas:
- The ability to maintain defensive lines as pressure is mounting
- Reconstruction of damaged infrastructure before or during winter
- Development of new tactical approaches, to counter pre-existing ones Integration of emerging technologies, as war forces both parties to race against one another in research and development
- Sustainability of current force levels, which becomes particularly difficult as both parties suffer casualties
In parallel, Reisner makes note of the strategic factors:
- Western political unity and support, especially poignant in a period of uncertainty after the recent result of the US elections
- Russian domestic stability, as Russia cannot fight a ‘’forever war’’ without approaching breaking point
- Regional security dynamics, with outside parties suddenly sending troops to Ukraine
- Evolution of military technology, possibly providing opportunities to force a breakthrough, as hinted at by Zaluzhnyi in the past
- And lastly, general global economic conditions impacting the war as a whole
The conflict has broader implications for global security and international relations that extend far beyond the immediate battlefield.
It has highlighted shifting power dynamics between the global North and South, with many developing nations choosing not to align with Western positions on the war. This realignment suggests a fundamental shift in the international order that may outlast the current conflict.
The war has also forced a reassessment of military doctrines and capabilities among Western nations. The importance of industrial capacity in modern warfare has been starkly demonstrated, raising questions about Western defense industrial capabilities and the ability to sustain high-intensity conflicts.
Reisner concludes with a stark warning about the broader implications of the war:
"This isn't just about Ukraine. We're witnessing a fundamental shift in global power dynamics, with implications far beyond the immediate battlefield."
The war’s outcome may well determine the future of international relations and military affairs, making it essential for Western nations to carefully consider their level of commitment and strategic objectives in supporting Ukraine.
Related:
- Ukraine develops unjammable fiber optic FPV attack drone, catching up to Russia’s innovation
- Why is Ukraine losing ground? Mobilization crisis and command failures exposed
- Ukraine strikes Russian-occupied gas platform in Black Sea used for electronic warfare
- Russian naval presence in northwestern Black Sea ended in 2023, Ukraine Navy commander says
- Rutte: NATO will do what’s necessary to ensure Ukraine’s victory





