According to the study, the German economy suffers by far the largest export losses among the Western Nations due to the sanctions against Russia, the newspaper Rheinische Post reported, citing an unpublished investigation of the Kiel Institute for the World Economy (IfW).
"Germany accounts for almost 40% of lost trade in the West, while other major geopolitical players such as the United Kingdom (7.9%), France (4.1%) and the United States (0.6%) are far less affected," reads the study.

According to the calculations of the Kiel Institute, German exports are on average about 727 million dollars (618 million euros) per month lower than in the scenario without sanctions. According to the IfW calculations, the total cost of the sanctions imposed on Russia in 2014 was $ 114 billion (€ 97 billion) in 2015 alone, with 61% attributable to Russian companies. The export loss of the sanctioning western countries amounted to 44 billion dollars (37.5 billion euros), of which 90% fell to the EU countries.
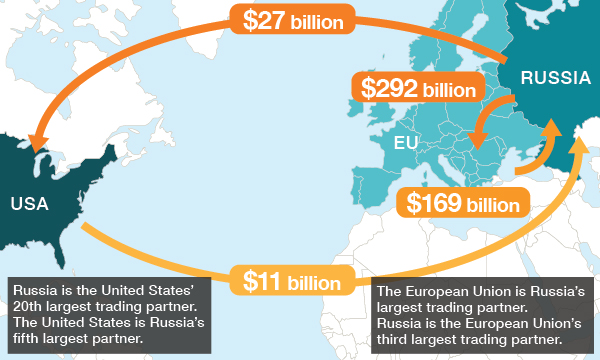
- The EU imposed various sanctions on Russia since the annexation of the Ukrainian region of the Crimea back in 2014.
- In addition to sanctions against individuals and organizations, there are sanctions against parts of the Russian economy.
The EU economic sanctions on Russia:
- limit access to EU capital markets for major Russian state-owned financial institutions and energy and defense companies;
- ban both the export and import of arms;
- ban the export of dual-use goods for military use to Russia;
- curtail Russia’s access to certain sensitive technologies and services that can be used for oil production and exploration.
Editor's Note
On 14 December 2017, the European Union has once again extended sanctions against Russia because of the stalled peace process in Ukraine.
In terms of Russia as a whole, if former Russian Finance Minister Alexey Kudrin is to be believed, sanctions cost Russia 1.5% of GDP, which aligns with the IMF, which estimates that ”…sanctions and counter-sanctions might have initially reduced real GDP by 1 to 1½ percent. Prolonged sanctions may compound already declining productivity growth. The cumulative output loss could amount to 9 percent of GDP over the medium term.”
In 2014, Russia has also imposed and keeps extending counter-sanctions on the Western countries. These involve introducing travel bans against a blacklist of 89 EU politicians and military leaders as well as blocking imports of selected categories of agro-food products from the EU, US, Australia, Japan, and other countries that had previously imposed economic sanctions on Russia.
Read more:
- Rest assured, Marine Le Pen, sanctions against Russia work
- US sanctions on Russia effective, don’t hurt American economy, report finds
- The treason of Europe: PACE adopts resolution allowing to lift political sanctions against Russia
- EU Parliament demands Russia release 47 Ukrainian de facto political prisoners
- Arms race, on top of sanctions, destroyed the USSR and will destroy Russia
- Russia considering introducing Islamic banking to get around Western sanctions
- Siemens’ Crimea sanctions break – a case of criminal negligence | #SiemensGate
- Trump and Russian sanctions
- EU sanctions keep Putin’s associate from entering Moldova
- EU prolongs sanctions over actions against Ukraine’s territorial integrity
- USA sanctions against Russia renewed and reinforced. Key things to know
- Powering the Anschluss. How Siemens turbines ended up in Crimea despite sanctions
- Ukraine extends sanctions, blocks popular Russian web services and software companies
- Scandal as Dutch companies help build bridge to occupied Crimea, violating sanctions
- Ukraine considers sanctions against officials behind media crackdown in occupied Crimea
- Armenia is the Vichy France of today, Khzmalyan says
- Recent US survey shows American public in favor of stronger sanctions on Russia
- European Parliament: Russia should free all the illegally imprisoned Ukrainians #LetMyPeopleGo





