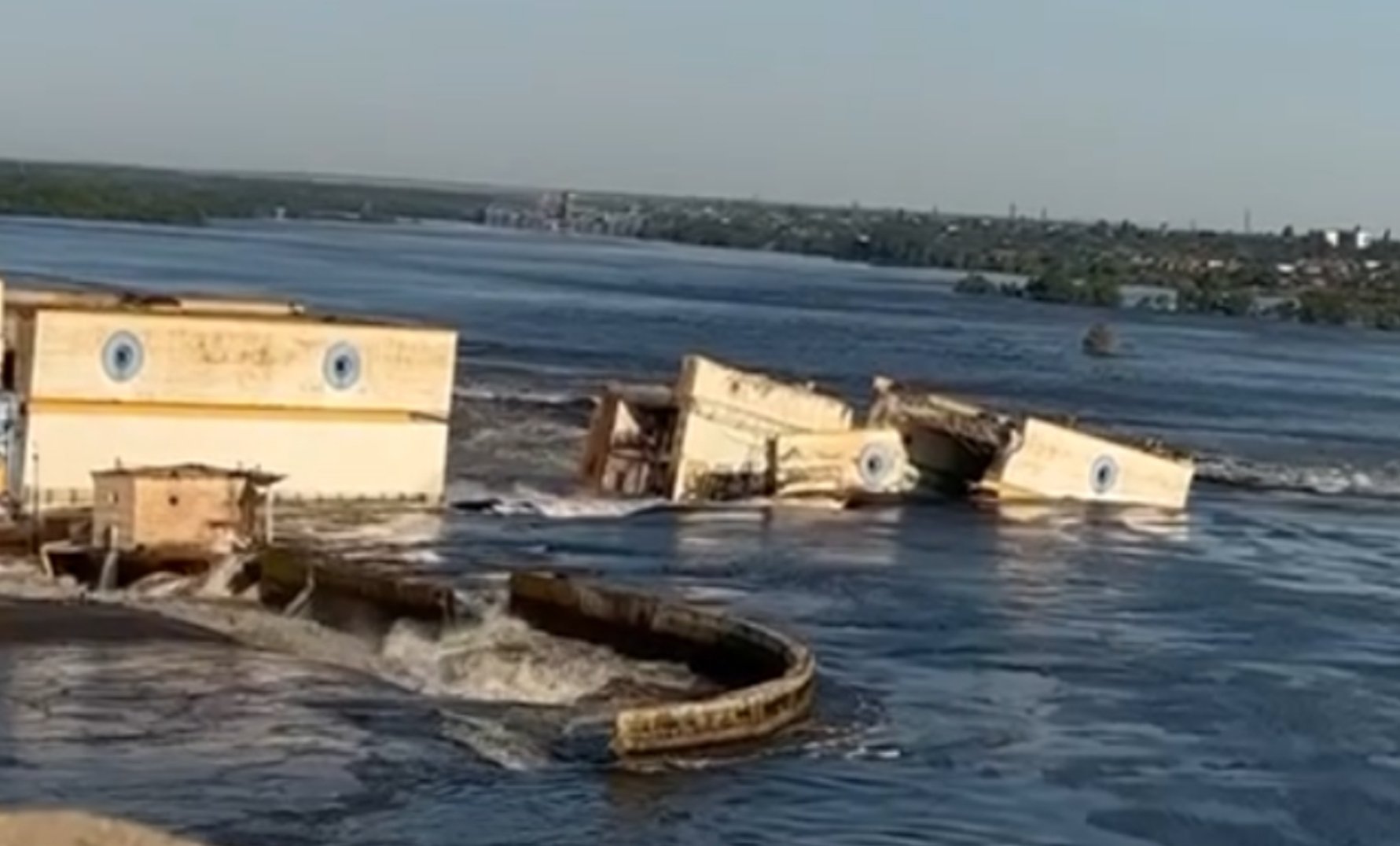
Forbes analyst Volodymyr Dacenko offers seven reasons for why any version outside of Russia's deliberate destruction of the Kakhovka dam on 6 June, resulting in immense flooding, should be discarded.
1. The water discharge patterns gave no indication that the Kakhovka dam was weak
Some believe that the dam collapsed on its own due to previous damage. Satellite images of water discharge are cited as evidence.
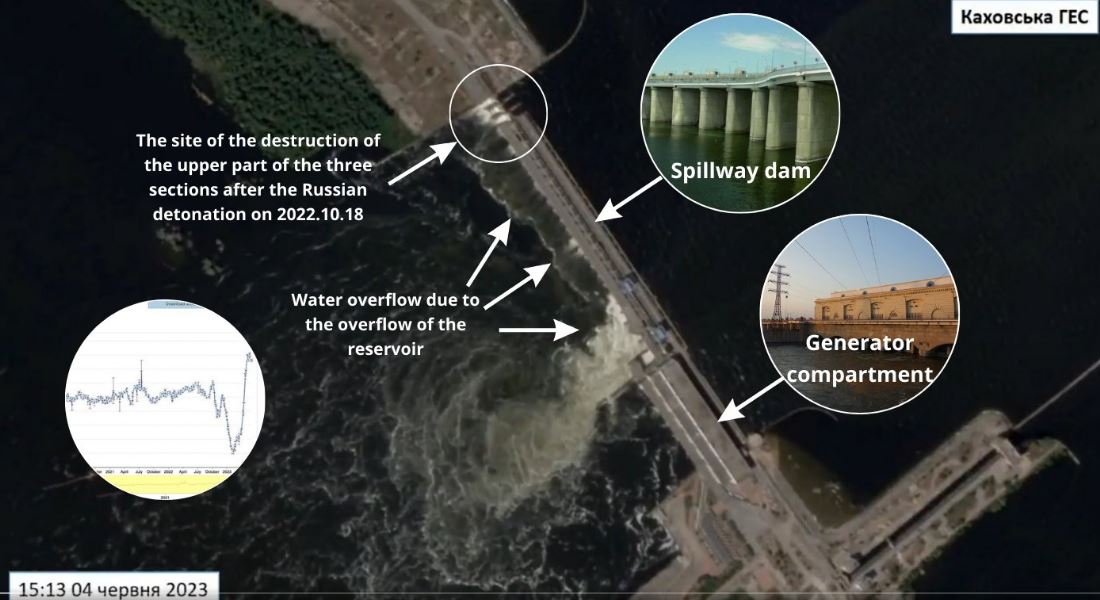
But it suffices to look at satellite images from last year (before the first time that the Russians partially blew up the Kakhovka HPP on 18 October 2022) to verify that the pattern of water discharge was identical and does not indicate damage to the dam.
For comparison, a picture of the HPP on 15 October 2022 and 5 June 2023 (where there are allegedly signs of the bad condition of the HPP).

2. The epicenter of destruction is far from the place the dam was the weakest
The destruction of the HPP is not of a cascading nature but zonal, and the epicenters of the destruction are far from the place of detonation on 18 October 2022. During last year's retreat, the Russians blew up the upper part above the three sluice gates on the right bank side.
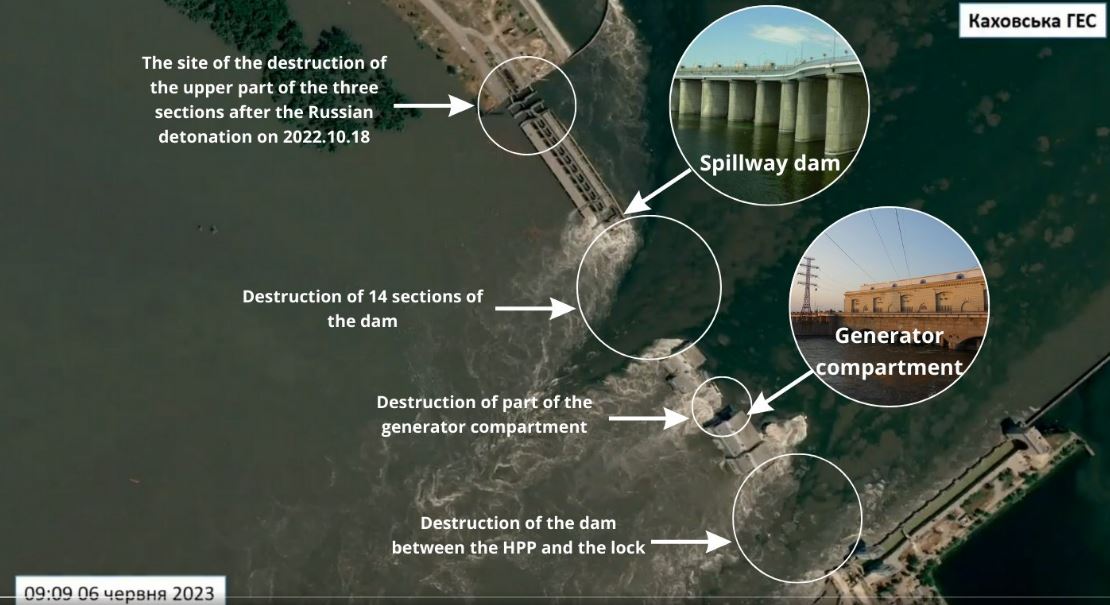
Now about 14 sections of the dam on the other side of the previous explosion, the engine room, and the dam between the HPP and the lock are destroyed. Accordingly, there is no cascading nature of destruction.
3. Self-destruction would have started from the sluice gates
The structure of the HPP is not monolithic, and therefore the cascading nature of the destruction should not, in principle, occur. In essence, each section that holds the sluice gate is a separate reinforced concrete support.
That is, damage to one support does not lead to damage to another. Metal shields are a much more vulnerable part of the dam than reinforced concrete supports, and self-destruction would have a completely different appearance - the collapse of the shields.
4. Russians pumped up the water levels to the utmost, preparing for detonation
The Russians deliberately kept the water level in the reservoir at the maximum. First, to fill the reservoirs in Crimea as much as possible. Secondly, to achieve the maximum flood wave. The time of the detonation was also chosen for this purpose.
5. The Kakhovka hydropower plant was built to withstand a nuclear strike
I am attaching photos of the construction of the HPP to demonstrate the scale of the structure and safety margin. It is very difficult to believe that the engine room was "washed away with water." And it is not clear why it was "washed away" not from the side of the previous explosion, but from the side of the left bank.

- Historic imagery of the construction of the dam in Nova Kakhovka reveal the sturdiness of the structures
6. Soviets needed 20 tons of explosives to destroy Kakhovka HPP 1.0
The Kakhovska HPP cannot be destroyed in any other way than by placing a large amount of explosive charge in the base of the structure. During the first detonation of the old Kakhovska HPP in 1941, the Soviet authorities needed 20 tons of explosives.
Therefore, the story about the "hit" on the hydroelectric power plant and the dam's destruction by the 93-kilogram GMLRS is an even bigger fiction than the story about "self-destruction."
7. Russia controlled the plant all this time
It was Russia that controlled the HPP all this time. Russia blew up the dam for the first time on 18 October 2022. Russia kept the water level in the reservoir at a maximum. It is impossible to believe that someone could plant several tons of explosives unnoticed by the Russians. Russia did it on purpose and tried to achieve the maximum effect of its crime.
- Earwitnesses heard profound explosions that were unlike any artillery fire they ever heard;
- Seismic stations registered an explosion on 6 June;
- Russian soldiers mentioned that the dam's destruction was their own work in an audio intercept shared by the SBU;
- Engineers explain how the dam was built to withstand a nuclear strike amid the Cold War.
Related:
- Ukraine now probably has as many tanks as Russia
- Russia’s losses in Ukraine dwarf those of past conflicts, analyst finds
- Study shows drones the cheapest, most effective in battle against Russian invasion
- Earwitnesses recall hearing explosions on night when Nova Kakhovka dam collapsed
- Seismic signals indicate Kakhovka dam explosion – NORSAR
- Russian sabotage group blew up Kakhovka dam; it didn’t go as planned, SBU intercept alleges
- Kakhovka Dam was built to withstand nuclear strike, couldn’t be destroyed from outside – Ukrhydroproject engineering company
- Kakhovka dam breach: Hundreds of Ukrainians drown as Russia prevents evacuation, seals off flooded towns

