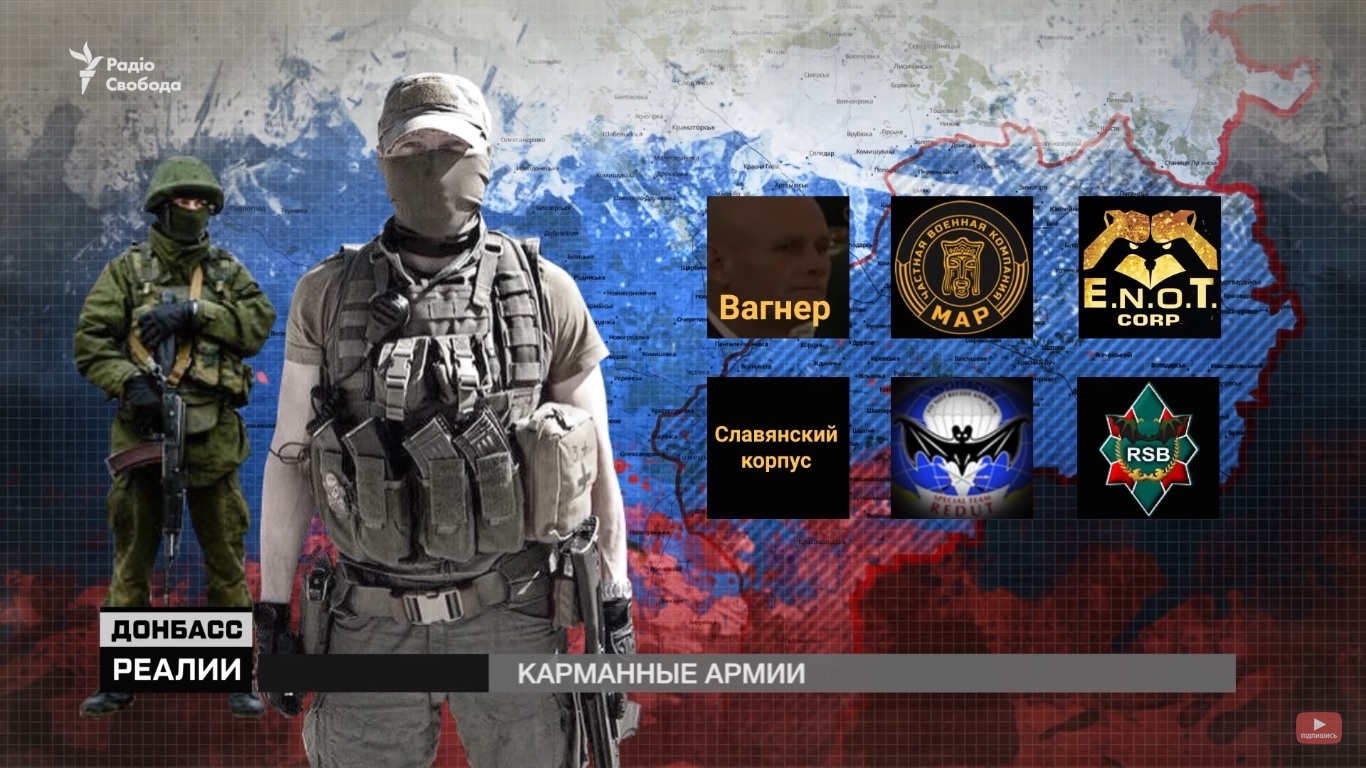
The Russian State Duma will soon be taking up draft legislation regularizing the status of nominally “private” military companies, even though such mercenaries are banned by Russian law. And among the first places they may be deployed is the part of Ukraine’s Donbas currently occupied by Russia, according to Kyiv observer Oleksiy Kaftan.

In his commentary in Delovaya stolitsa, he says that the way the new law has been proposed highlights the problems Moscow faces regardless of whether it legalizes these private armies or not but that the timing represents a Russian response to the Ukrainian Verkhovna Rada’s declaration that Moscow is in occupation of Ukrainian territory.
On Monday, Kaftan reports, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov expressed his “personal” opinion that Russia needs a law governing private military companies so that the people taking part in them will be “within the legal field and thus protected” by the power of the state.
On Wednesday a senior Duma member said that the Russian legislature would take up a draft of this measure later this month, an indication Kaftan says that a final version either exists or is close to being drafted. And on Thursday, Putin’s press secretary supported the idea but noted that it wasn’t within the Kremlin’s purview and thus was not a Kremlin initiative.
There are good reasons for the Kremlin’s public restraint, Kaftan continues.
Hence it wants to be able to use private military companies instead.
The death of a private military company contractor will attract less notice and concern among Russians, but Moscow has a problem: its preferred “instrument of Kremlin geopolitics is illegal in the Russian Federation. Paragraph 359 of the criminal code calls for a punishment of from three to seven years for those who take part in military conflicts as mercenaries.
Of course, Kaftan continues, in the case of Russia, “the term ‘private’ … is a figure of speech” because if Moscow organizes them they aren’t private and if it doesn’t they aren’t legal.
What Moscow is moving to do is to make that “official.”
As the Duma deputy pushing the measures observes, “the law will allow getting employees of private military companies to take part in counter-terrorist operations abroad and in actions in defense of the sovereignty of allied governments from external aggression.” They can also be used to defend “various objects” including oil and gas wells and railways.

Head of the Conflict Intelligence Team (CIT)
In some of these cases, they will be in more or less open competition with regular Russian military units. But “there is a niche in which Russian private military companies will be beyond any competition.” Ruslan Leviev, the head of the Conflict Intelligence Team, says that they can be used in “the self-proclaimed republics of the Donbas, Abkhazia, South Ossetia and the countries of Central Asia.”
It is not likely to be a coincidence that this discussion began in Moscow on the eve of the Verkhovna Rada’s discussion of a law on the reintegration of the Donbas.” The Russian government appears to have decided that it will “formally withdraw” its defense ministry and FSB forces from that Ukrainian region and make use of “private military companies” instead.
But Moscow is making a big mistake if it thinks it can get away with this, Kaftan says. By ensuring that the private military companies are part of the Russian legal field, the Russian government has ensured that everyone will recognize that “Moscow all the same continues to bear responsibility for their actions.”
Read More:
- Ukraine names over 150 mercenaries from “Putin’s private army” fighting in Ukraine and Syria
- Wagner mercenaries: what we know about Putin’s private army in Donbas
- Moscow’s private military companies continue to be a serious threat in Ukraine
- Russian participation in the war in Donbas: evidence from 2017
- New UN resolution on Crimea confirms Russia is an occupying power, brings 10 important changes for Ukraine
- Portnikov: Putin has four Donbas scenarios and will choose worst one for Ukraine